Both laser cutting and wire cut EDM are important precision cutting technologies in modern manufacturing, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we’ll discuss their differences.
I. Working Principle
II. Applicable Materials
III. Comparisons
IV. Applications
V. Summary
VI. Questions
I. Working Principle
1. Laser Cutting
Principle: The heat generated by a high-energy laser beam instantly melts/vaporizes the material, achieving cutting, and an airflow removes the slag.
Features: No contact with the material, minimal thermal impact, and high speed.
2. Wire Cut EDM
Principle: A moving metal wire (molybdenum, copper, or alloy) creates a pulsed electric spark discharge between the material and the material, generating high temperatures that melt/vaporize the material, achieving cutting.
Features: No mechanical stress, capable of cutting high-hardness conductive materials. https://youtu.be/NRhUJI5sFYw
II. Applicable Materials
1. Laser Cutting
Metals: Carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum and copper. Aluminum requires special lasers. Copper requires high reflectivity and high power, etc.
Non-metals: Wood, plastic, ceramics, acrylic, etc. Ceramics uses special lasers.
Limitations: It cannot cut highly reflective materials, such as pure copper and gold. It can’t cut transparent materials, such as glass.
2. Wire Cut EDM
Conductive materials only: Steel, carbide, graphite, titanium alloy, and other conductive materials.
No hardness restrictions: Can cut ultra-hard materials (such as mold steel).
Limitations: Cannot cut non-conductive materials such as ceramics, plastics, and fabric.
III. Differences and Comparisons
| Item | Laser Cutting | Wire Cut EDM |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Metal material: ≤30mm It can cut thicker non metal material. | >=300mm |
| Cutting accuracy | ±0.1mm | ±0.005mm |
| Surface | Narrow kerf, may cause oxidation | No heat impact, smooth surface |
| Speed | Fast, especially cutting thin plate | Slower.It depends on discharge efficiency |
| Thermal Impact | May cause thermal deformation | Almost has no thermal deformation |
| Cost | The machine is expensive. High efficiency, no consumables | High consumables-electrode wire and time costs |
| Shape Limitation | Any graphic | Suitable for high-precision complex molds and filter parts. Such as gears, special holes, sintered mesh filter parts |
IV. Applications
1. Laser Cutting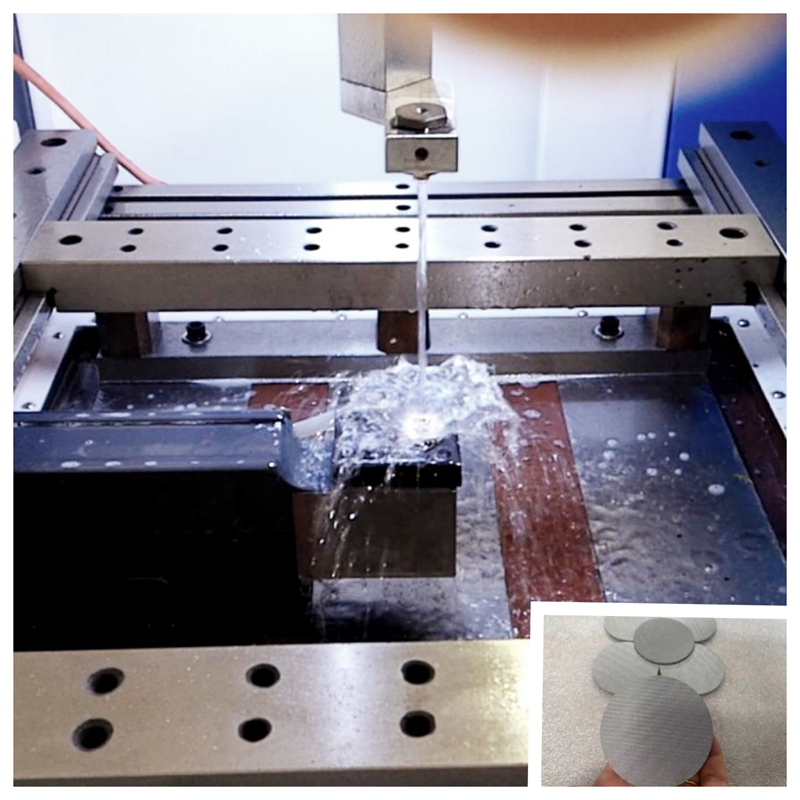
It is particularly suitable for thin plates such as extruder discs, profile perforations to replace perforated or punched process, boxes, sheet metal parts, , advertising fonts, and handicrafts. It is suitable for large-scale production, complex shapes, and high efficiency.
2. Wire Cut EDM
It is primarily used for high-precision, vertical cutting without bevels on ultra-hard materials or thick work-pieces such as sintered laminted wire mesh, molds, large gears, tungsten carbide, and hardened steel. It is suitable for small batches, single items, or sample processing.
Summary
Suitable for laser cutting: If you require high-volume, high-efficiency cutting with complex shapes, especially when designing non-metallic or thin metal sheets, laser cutting is the preferred method due to its high speed and wide applicability. The stainless steel mesh is thin. Some customers require high cutting accuracy. We use laser cutting machine to make the filter discs.
Suitbale for wire cut EDM: If you require small-volume, thick sheet metal cutting with high precision, wire cutting is the preferred method, especially for high-hardness conductive materials. The sintered multi layer mesh is thick. And customer has high requirement on tolerance. We use wire cut EDM to make it.
Question
What are the respective development trends and directions for laser cutting and wire cut EDM?
In the field of thin metal cutting, laser cutting dominates, especially for box and profile processing.
Wire cutting is primarily used in mold making and offers significant advantages in high-precision, ultra-thick sheet metal cutting.


